Extension of the Zwin
Control measures for saline water.

Agentschap Mariene Dienstverlening en Kust - Provincie Zeeland
28 February 2019
A Flemish-Dutch collaboration
The Flemish and the Dutch governments decided to enlarge the Zwin lagoon area by 120 hectares. By the extension a new natural area would be created and the flood risk of the hinterland would be reduced. The extension is also accompanied by a widening and deepening of the Zwin gully in order to prevent accumulation of deposits in the Zwin.
Adjustment of the polder landscape
In order to expand the flood area, the existing dyke had to be demolished and a new dyke complex had to be built in the Willem-Leopold polder. This was accompanied by the construction of new viewpoints and walking and cycling paths. In addition, a new breeding island has been built in the flood plain.


The salt danger
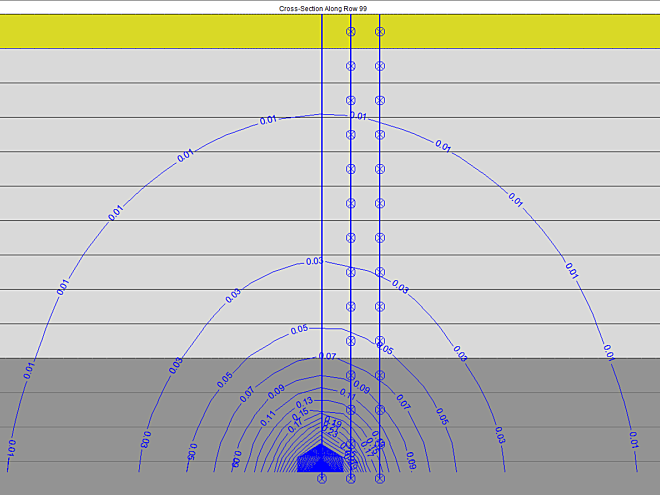
Since the flooding level is higher than the average groundwater level in the surrounding of the polders, an increased salt groundwater intrusion was expected from the new flood area in the direction of the surrounding agricultural plots. Therefore, a management plan was prepared in order to prevent the salinization of the shallow groundwater body and protect the fertility of the neighbouring agricultural area.

Monitoring
Geophysical measurements were carried out before and during the works. In addition, both the groundwater level and the water level in the canals were monitored at several observation points. This monitoring network remains active even after completion in order to monitor the hydrogeological changes in detail.

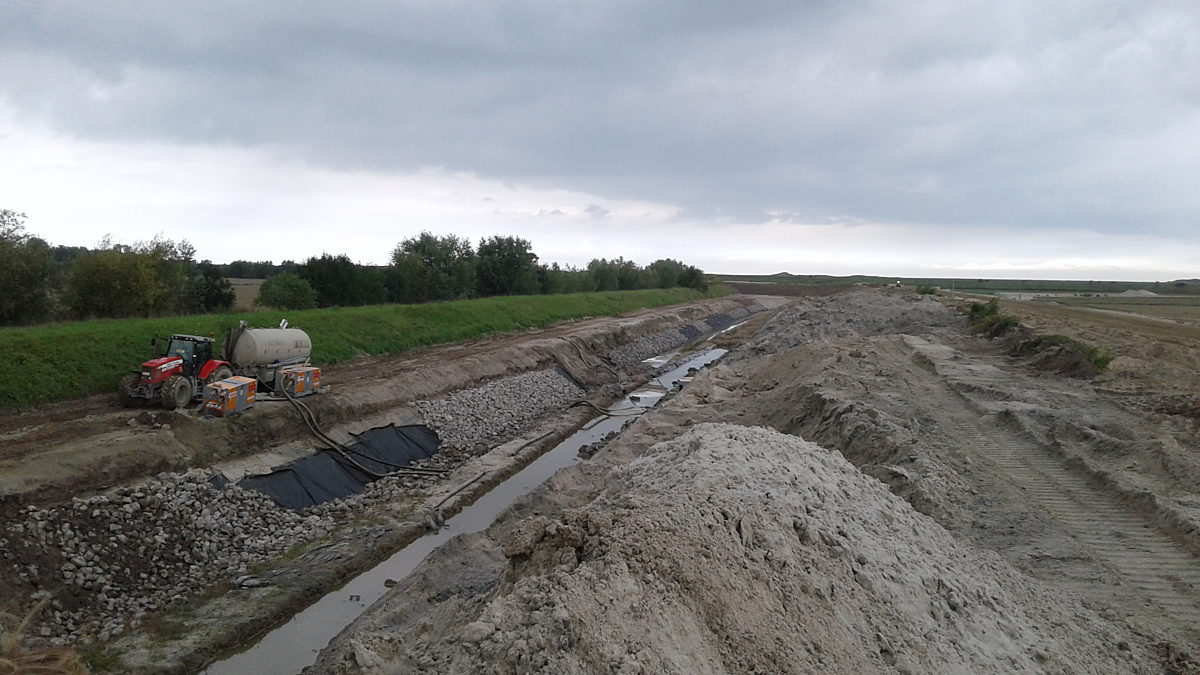
Protection of the polder
The management plan includes the construction of a draining canal to capture the salt water intrusion, a freshwater infiltration canal, and possibly saltwater capture wells. AGT assessed the effect of these measures with field measurements and hydrogeological modelling. The field measurements included additional CPT measurements, pumping tests as well as drainage and infiltration tests along the canals. These measurements allowed to estimate the critical parameters of the substrate.

 Brussel
Brussel